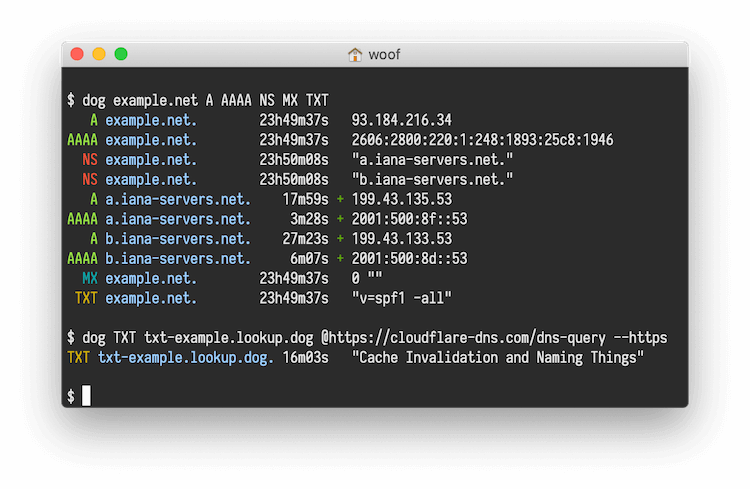
Dog is a command-line DNS client, like dig. It has colourful output, understands normal command-line argument syntax, supports the DNS-over-TLS and DNS-over-HTTPS protocols, and can emit JSON.
Examples
- dog example.net Query a domain using default settings
- dog example.net MX …looking up MX records instead
- dog example.net MX @1.1.1.1 …using a specific nameserver instead
- dog example.net MX @1.1.1.1 -T …using TCP rather than UDP
- dog -q example.net -t MX -n 1.1.1.1 -T As above, but using explicit arguments
Command-line options
Query options
<arguments> Human-readable host names, nameservers, types, or classes
-q, –query=HOST Host name or IP address to query
-t, –type=TYPE Type of the DNS record being queried (A, MX, NS…)
-n, –nameserver=ADDR Address of the nameserver to send packets to
–class=CLASS Network class of the DNS record being queried (IN, CH, HS)
Sending options
–edns=SETTING Whether to OPT in to EDNS (disable, hide, show)
–txid=NUMBER Set the transaction ID to a specific value
-Z=TWEAKS Set uncommon protocol-level tweaks
Protocol options
-U, –udp Use the DNS protocol over UDP
-T, –tcp Use the DNS protocol over TCP
-S, –tls Use the DNS-over-TLS protocol
-H, –https Use the DNS-over-HTTPS protocol
Output options
-1, –short Short mode: display nothing but the first result
-J, –json Display the output as JSON
–color, –colour=WHEN When to colourise the output (always, automatic, never)
–seconds Do not format durations, display them as seconds
–time Print how long the response took to arrive
Installation
To install dog, you can download a pre-compiled binary, or you can compile it from source. You may be able to install dog using your OS’s package manager, depending on your platform.
Also See- Termshark: To Analyze Network Traffic
Packages
For Arch Linux, install the dog-dns package from the AUR.
For Homebrew on macOS, install the dog formula.
Downloads
Binary downloads of dog are available from the releases section on GitHub for 64-bit Windows, macOS, and Linux targets. They contain the compiled executable, the manual page, and shell completions.
Compilation
dog is written in Rust. You will need rustc version 1.45.0 or higher. The recommended way to install Rust for development is from the official download page, using rustup.
To build, download the source code and run:
$ cargo build $ cargo test
The just command runner can be used to run some helpful development commands, in a manner similar to make. Run just –tasks to get an overview of what’s available.
If you are compiling a copy for yourself, be sure to run cargo build –release or just build-release to benefit from release-mode optimisations. Copy the resulting binary, which will be in the target/release directory, into a folder in your $PATH. /usr/local/bin is usually a good choice.
To compile and install the manual pages, you will need pandoc. The just man command will compile the Markdown into manual pages, which it will place in the target/man directory. To use them, copy them into a directory that man will read. /usr/local/share/man is usually a good choice.
Testing
dog has an integration test suite written as Specsheet check documents. If you have a copy installed, you can run:
just xtests
Specsheet will test the compiled binary by making DNS requests over the network, checking that dog returns results and does not crash.
Documentation
For documentation on how to use dog, see the website: https://dns.lookup.dog/